Cancer Education and Research Institute® (CERI)'s Cancer Education Programs
Our Team of cancer experts at Cancer Education and Research Institute® (CERI)'s, formerly Cancer Research Simplified, provides you with the most reliable, most up-to-date, and simplified cancer information available. Our educational programs quickly became trusted and highly sought after worldwide.
CERI strongly stands behind the importance of cancer patient empowerment and is a worldwide leading source for simplified, multi-language cancer education. Knowledge is power and empowerment is the key for greater treatment success, early diagnosis, as well as cancer prevention.
For any questions or requests, please submit your inquiry at our CERI Personalized Patient Program™ page.
CERI strongly stands behind the importance of cancer patient empowerment and is a worldwide leading source for simplified, multi-language cancer education. Knowledge is power and empowerment is the key for greater treatment success, early diagnosis, as well as cancer prevention.
For any questions or requests, please submit your inquiry at our CERI Personalized Patient Program™ page.
Head and Neck Cancers
|
Head and neck cancers include cancers of the larynx, throat, lips, mouth, nose, and salivary glands. It affects vital functions such as speech, swallowing, breathing, and appearance. Tobacco use, heavy alcohol use, and infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV) increase the risk of head and neck cancer.
|
What are Head and Neck Cancers?
 Copyright © All rights reserved - Cancer Education and Research Institute, Inc.
Copyright © All rights reserved - Cancer Education and Research Institute, Inc.
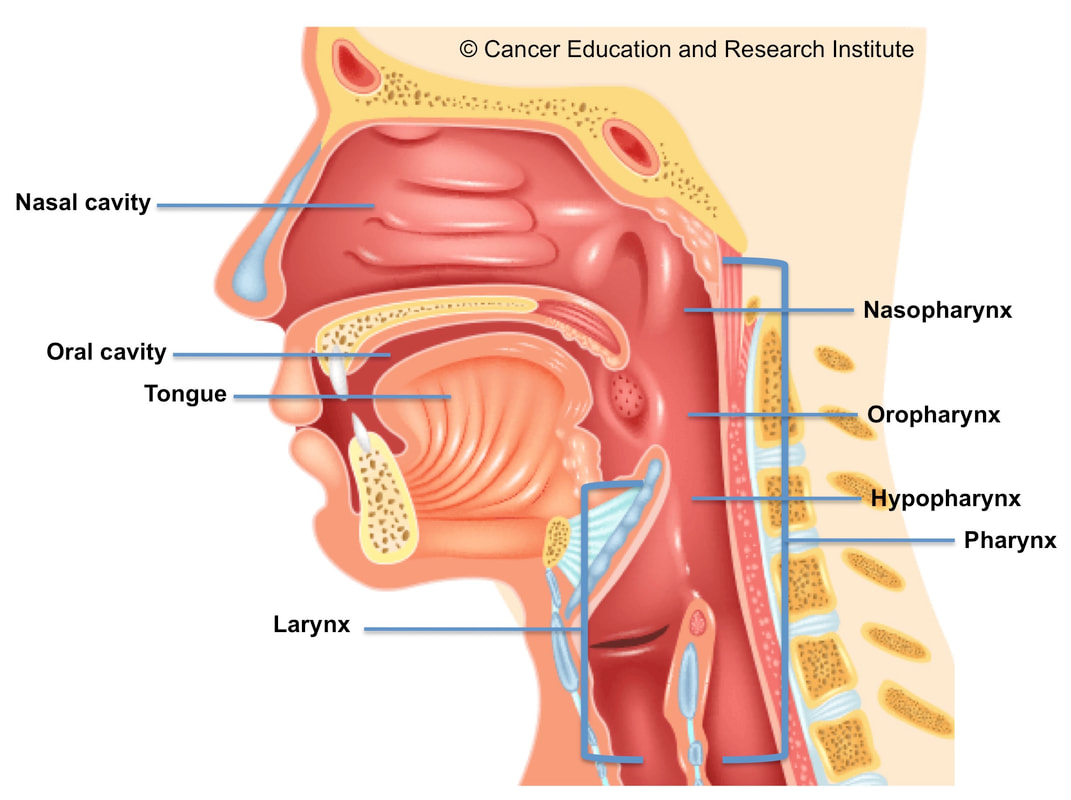
Head and neck cancers are classified by the head or neck region where they start. These areas are defined below:
Oral cavity: Lips, two-thirds of the tongue, gums, lining inside the cheeks and lips, floor of the mouth under the tongue, small area on the palate and behind the wisdom teeth.
Pharynx: The pharynx (throat) is a hollow tube about 13 cm long that starts at the back of the nose and goes into the esophagus. It consists of three parts: the nasopharynx (upper part of the pharynx, back of the nose); oropharynx (including the middle part of the pharynx, back of the mouth, base of the tongue and tonsils); hypopharynx (lower part of the pharynx).
Larynx: The larynx, also called the voice box, is a short passage formed by the cartilage just below the pharynx in the neck. The larynx contains the vocal cords. It also has a small tissue called the epiglottis that acts to line the larynx to prevent food from entering the airways.
Paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity: Paranasal sinuses are hollow small spaces in the bones of the head that surround the nose. The nasal cavity is the hollow space inside the nose.
Salivary glands: The major salivary glands are located on the floor of the mouth and near the jawbone. The salivary glands produce saliva.
Oral cavity: Lips, two-thirds of the tongue, gums, lining inside the cheeks and lips, floor of the mouth under the tongue, small area on the palate and behind the wisdom teeth.
Pharynx: The pharynx (throat) is a hollow tube about 13 cm long that starts at the back of the nose and goes into the esophagus. It consists of three parts: the nasopharynx (upper part of the pharynx, back of the nose); oropharynx (including the middle part of the pharynx, back of the mouth, base of the tongue and tonsils); hypopharynx (lower part of the pharynx).
Larynx: The larynx, also called the voice box, is a short passage formed by the cartilage just below the pharynx in the neck. The larynx contains the vocal cords. It also has a small tissue called the epiglottis that acts to line the larynx to prevent food from entering the airways.
Paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity: Paranasal sinuses are hollow small spaces in the bones of the head that surround the nose. The nasal cavity is the hollow space inside the nose.
Salivary glands: The major salivary glands are located on the floor of the mouth and near the jawbone. The salivary glands produce saliva.
What are the Causes of Head and Neck Cancers?
- Alcohol and tobacco use, especially “tobacco chewing”. At least 75% of head and neck cancers are caused by tobacco and alcohol use. People who use both tobacco and alcohol are at greater risk of developing these cancers than people who use tobacco or alcohol alone.
- Infection with cancer-causing human papillomavirus types (HPV).
Other factors can be listed as follows:
- Betel. Keeping betel in your mouth.
- Preserved or salty foods. Consumption of certain preserved or salted foods during childhood is a risk factor for nasopharyngeal cancer.
- Oral health. Poor oral hygiene and missing teeth may be poor risk factors for oral cavity cancers.
- Occupational exposure. Occupational exposure to wood dust is a risk factor for nasopharyngeal cancer.
- Radiation exposure. Radiation to the head and neck for non-cancerous conditions or cancer is a risk factor for cancer of the salivary glands.
- Epstein-Barr virus infection. Infection with Epstein-Barr virus is a risk factor for nasopharyngeal cancer and cancer of the salivary glands.
- Genetics. People of Asian descent, especially Chinese descent, have an risked risk in developing nasopharyngeal cancer.
What are the symptoms of head and neck cancers?
Symptoms of head and neck cancers may include a lump that does not heal or a sore, non-healing throat, difficulty swallowing, and a change in voice or hoarseness. These symptoms can also be caused by other less serious conditions. It is important to check with your physician or dentist for any of these symptoms.
Symptoms that can affect certain areas of the head and neck include:
Oral cavity:
Pharynx:
Larynx:
Paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity:
Salivary glands:
Symptoms that can affect certain areas of the head and neck include:
Oral cavity:
- A white or red sore on the gums, tongue, or lining of the mouth
- Swelling of the jaw causing poor fit or discomfort of the dentures
- Unusual bleeding or pain in the mouth
Pharynx:
- Trouble breathing or speaking
- Pain when swallowing
- Pain that does not go away in the neck or throat
- Frequent headaches, pain or ringing in the ears
- Having trouble hearing
Larynx:
- Pain or earache when swallowing
Paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity:
- Blocked and not cleared sinuses
- Chronic sinus infections that do not respond to treatment with antibiotics
- Bleeding from the nose
- Frequent headaches, swelling of the eyes or other problems
- Pain in the upper teeth
- Problems with dentures
Salivary glands:
- Swelling under the chin or around the jawbone
- Numbness or paralysis of facial muscles or facial pain
- Pain in the jaw or neck that does not go away
Who is More Likely to Get Head and Neck Cancers?
Head and neck cancers are two times more common in men than in women. In addition, head and neck cancers are diagnosed more often in people over the age of 50 than in younger people.
How are Head and Neck Cancers Diagnosed?
The physician will evaluate a patient's medical history, perform a physical exam, and order diagnostic tests.
If the diagnosis is cancer, the physician will want to know the stage (or degree) of the disease. Staging may include examination under anesthesia in the operating room, X-rays and other imaging procedures, and laboratory tests. Knowing the stage of the disease is important for the physician to plan the treatment.
If the diagnosis is cancer, the physician will want to know the stage (or degree) of the disease. Staging may include examination under anesthesia in the operating room, X-rays and other imaging procedures, and laboratory tests. Knowing the stage of the disease is important for the physician to plan the treatment.
How are Head and Neck Cancers Treated?
The treatment plan for an individual patient depends on many factors, including the exact location of the tumor, the stage of the cancer, the person's age and general health. Treatment for head and neck cancer:
People diagnosed with HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer may be treated differently than people with HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancer. Recent research has shown that patients with HPV-positive oropharyngeal tumors have a better prognosis and less intensive treatments can be undertaken. However, research on this subject continues.
The most common treatment for head and neck cancer is surgery. Some tumors can be removed with minimally invasive procedures. These include laser microsurgery, robotic approaches, and Mohs surgery.
Other times, head and neck cancer surgeries can be very complex. They require careful preparation and planning. For this reason, head and neck cancer is treated by specialist surgeons and doctors with extensive experience in cancer treatment.
Radiation to the head and neck can cure many people with the disease. Radiation oncologists use many advanced technologies to treat head and neck cancer.
Immunotherapy:
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) are monoclonal antibodies that target cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4), programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1), or PD-1 ligand (PD-L1). ICI is also approved for the treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. ICI can cause long-term anti-tumor responses by disabling the braking mechanism in the immune system. Ipilimumab, tremelimumab, pembrolizumab, nivolumab, atezolizumab, durvalumab, and avelumab are examples of ICI.
Additional Information for Immunotherapy: Immune checkpoint inhibitors are the body's natural immune system control mechanism, they work as a kind of brake. Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) and its activating protein, namely PD-1 ligand (PD-L1) and the protein called cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4), are the most well-known of these inhibitors. These three proteins are currently used successfully in immunotherapy of cancer. Finding the importance of these three proteins for cancer treatment, Dr. Jim Allison won the Nobel Prize in 2018.
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy, or
- Combination of treatments
People diagnosed with HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer may be treated differently than people with HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancer. Recent research has shown that patients with HPV-positive oropharyngeal tumors have a better prognosis and less intensive treatments can be undertaken. However, research on this subject continues.
The most common treatment for head and neck cancer is surgery. Some tumors can be removed with minimally invasive procedures. These include laser microsurgery, robotic approaches, and Mohs surgery.
Other times, head and neck cancer surgeries can be very complex. They require careful preparation and planning. For this reason, head and neck cancer is treated by specialist surgeons and doctors with extensive experience in cancer treatment.
Radiation to the head and neck can cure many people with the disease. Radiation oncologists use many advanced technologies to treat head and neck cancer.
Immunotherapy:
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) are monoclonal antibodies that target cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4), programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1), or PD-1 ligand (PD-L1). ICI is also approved for the treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. ICI can cause long-term anti-tumor responses by disabling the braking mechanism in the immune system. Ipilimumab, tremelimumab, pembrolizumab, nivolumab, atezolizumab, durvalumab, and avelumab are examples of ICI.
Additional Information for Immunotherapy: Immune checkpoint inhibitors are the body's natural immune system control mechanism, they work as a kind of brake. Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) and its activating protein, namely PD-1 ligand (PD-L1) and the protein called cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4), are the most well-known of these inhibitors. These three proteins are currently used successfully in immunotherapy of cancer. Finding the importance of these three proteins for cancer treatment, Dr. Jim Allison won the Nobel Prize in 2018.
References:
- National Cancer Institute, cancer.gov, Accessed on 3/31/2019
- McCammon SD, J Surg Oncol. Mar 29, 2019.
- Simsek M, Tekin SB, Bilici M., Eurasian J Med. 2019 Feb;51(1):90-94.
- Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, Accessed on 4/1/2019
#Empowermentagainstcancer™ #CERICancerEducation #CERICares #CancerSimplified
GET YOUR FREE ARTICLE: Make sure to get your free article as our gift to you! Go to: canceredinstitute.org/ceri-simplified-cancer-research-articles
CORONAVIRUS PAGE: For our educational and up-to-date informational page on Coronavirus, go to: canceredinstitute.org/coronavirus
FOLLOW US for DAILY information and updates:
CORONAVIRUS PAGE: For our educational and up-to-date informational page on Coronavirus, go to: canceredinstitute.org/coronavirus
FOLLOW US for DAILY information and updates:
- INSTAGRAM: instagram.com/canceredinstitute
- FACEBOOK: facebook.com/canceredinstitute
- Twitter: twitter.com/canceredinst
- LinkedIn: linkedin.com/company/canceredinstitute
#headandneck #headandneckcancers #headandneckcancer #headandneckcancerawareness #headandneckcancerawarenessmonth #health #cancer #cancerawareness #cancereducation #cancerresearch #cancertreatment #immunotherapy #cancerimmunotherapy #checkpointinhibitor
You might also like:
|
|
|
Disclaimer: We can not assume responsibility of misinterpretation of content.
Please donate to support our program - help us save MORE lives!