The Journal of Simplified Cancer Research (JSCR) - New Article Release
FDA Approved Cancer Drugs in 2016
By Ayse Asiye Culum, MS, MS and Ayguen Sahin, MS, PhD, Cancer Education and Research Institute (CERI)
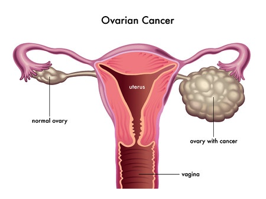 Figure 1. Ovarian cancer
Figure 1. Ovarian cancer
- Rubraca (rucaparib), December 19, 2016: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted an accelerated approval for Rubraca (rucaparib), a new treatment for advanced ovarian cancer (Fig. 1). The FDA approved Rubraca to treat women with advanced ovarian cancer who have been treated with two or more chemotherapies and whose tumors have BRCA gene mutation.1 BRCA genes, such as BRCA 1 and BRCA 2, are involved in repairing damaged DNA, thus, preventing tumor development. DNA damages can be caused by natural and medical radiation or other environmental exposures.2 The FDA also approved FoundationFocus CDxBRCA, a companion diagnostic for use with Rubraca. This test detects the presence of deleterious BRCA gene mutations in the tumor tissue of ovarian cancer patients. If one or more mutations are detected, the patient may be eligible for treatment with Rubrica. Rubraca is marketed by Clovis Oncology, Inc. based in Boulder, Colorado. The FoundationFocus CDxBRCA companion diagnostic test is marketed by Foundation Medicine, Inc. of Cambridge, Massachusetts.1
FDA approves new treatment for advanced ovarian cancer
LATEST: NEW TREATMENT FOR OVARIAN CANCER
OVARIAN CANCER TREATMENT
OVARIAN CANCER STAGES
OVARIAN CANCER DIAGNOSIS
OVARIAN CANCER SYMPTOMS
OVARIAN CANCER FACTS
What is OVARIAN CANCER? INTRO
Early diagnosis procedures: Cervical & Endometrial cancer
 Figure 2. Darzalex (daratumumab)
Figure 2. Darzalex (daratumumab)
- Darzalex (daratumumab), November 21, 2016: The FDA approved a cancer immunotherapy drug, Darzalex (daratumumab), in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, or bortezomib and dexamethasone, for the treatment of patients with multiple myeloma who have received at least one prior therapy such as proteasome inhibitor (PI) or an immunomodulatory agent therapy3. Multiple myeloma is a form of blood cancer that occurs in infection-fighting plasma cells (a type of white blood cell) found in the bone marrow. Darzalex (daratumumab) is a monoclonal antibody that targets a cell surface protein called CD38, which is highly and uniformly expressed on myeloma cells. Therefore, it makes a potential target in the treatment of myeloma4. Darzalex is manufactured by Janssen Biotech, Inc. in Horsham, Pennsylvania.5
 Figure 3. Opdivo (nivolumab)
Figure 3. Opdivo (nivolumab)
- Opdivo (nivolumab), November 10, 2016: Opdivo (nivolumab), a cancer immunotherapy drug, was approved for the treatment of patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN) with disease progression on or after a platinum-based therapy.6 Opdivo nivolumab) inhibits the programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1), a protein expressed on the cell surface, which blocks the body’s immune system from attacking tumors. Nivolumab, a monoclonal antibody to the PD-1 receptor, promotes antitumor immunity by removing this key negative regulator of T-cell activation.7 Opdivo is manufactured by Princeton, New Jersey-based Bristol-Myers Squibb Company.6
What is CARCINOMA?
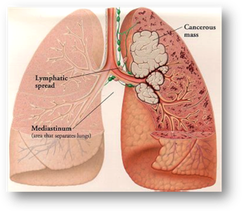 Figure 4. Non-small cell lung cancer11
Figure 4. Non-small cell lung cancer11
- Ketruda (pembrolizumab), October 24, 2016: The cancer immunotherapy drug, Keytruda (pembrolizumab), was approved for the treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors express PD-L1, the ligand for the PD-1 receptor8, as determined by an FDA-approved test called the PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmDx test, which is the the first test designed to detect PD-L1 expression in NSCLC 9. Pembrolizumab is a highly selective programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)-blocking antibody that has shown efficacy, leading to survival benefit and durable responses, in some patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)10. NSCLC is the most common type of lung cancer. Keytruda is marketed by Merck Sharp & Dohme Co., Inc. based in Kenilworth, New Jersey. The PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmDx diagnostic test is marketed by Dako North America Inc. in Carpinteria, California8.
 Figure 5: Lartruvo (olaratumab)
Figure 5: Lartruvo (olaratumab)
- Lartruvo (olaratumab), October 19, 2016: The FDA granted an accelerated approval of Lartruvo (olaratumab), a cancer immunotherapy drug, with doxorubicin to treat adults with certain types of soft tissue sarcoma (STS) cancers that develop in muscles, fat, tendons or other soft tissues. Lartruvo with doxorubicin is approved for the treatment of patients with STS who cannot be cured with radiation therapy or surgery and who have a type of STS for which an anthracycline (chemotherapy) is an appropriate treatment.12 Olaratumab is an antibody, which blocks the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor-alpha, inhibiting tumor development. PDGF receptors cause tumor growth when stimulated.13 Lartruvo is marketed by Eli Lilly and Company based in Indianapolis, Indiana.12
 Figure 6. Tarceva (erlotinib)
Figure 6. Tarceva (erlotinib)
- Tarceva (erlotinib), October 18, 2016: The indication for Tarceva (erlotinib) was modified by the FDA for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (Fig. 4) to limit the use for patients whose tumors have specific epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, including exon 19 deletions or exon 21 L858R substitution mutations.14 The regulation of protein kinases are impaired in most of the cancers.15 Tercava inhibits a tyrosine kinase, a molecular reaction catalyzing protein, associated with the human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Tarceva is marketed by Astellas Pharm Global Development Inc.14
 Figure 7. Tecentriq (atezolizumab)
Figure 7. Tecentriq (atezolizumab)
- Tecentriq (atezolizumab), October 18, 2016: Tecentriq (atezolizumab), a cancer immunotherapy drug, was approved to treat patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (Fig. 4) whose disease progressed during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy.16 Tecentriq inhibits the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway (proteins found on the body’s immune cells and some cancer cells) and may help the body’s immune system fight cancer cells by blocking these interactions. Tecentriq is marketed by Genentech based in San Francisco, California.
 Figure 8. Renal cell cancer
Figure 8. Renal cell cancer
- Opdivo (nivolumab), September 13, 2016: The FDA modified the dosage regimen for Opdivo (nivolumab) (see above) for the currently approved indications for renal cell carcinoma (Fig. 5), metastatic melanoma, and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)17 (Fig. 4).
- Keytruda (pembrolizumab), August 5, 2016: The FDA granted an accelerated approval for Keytruda (pembrolizumab) (see above) for the treatment of patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) with disease progression on or after platinium-containing chemotherapy.18
 Figure 9. cobas® EGFR Mutation test v2
Figure 9. cobas® EGFR Mutation test v2
- cobas® EGFR Mutation test v2, June 1, 2016: The FDA approved cobas® EGFR Mutation test v2 (Fig. 9) using plasma specimens as a companion diagnostic test for the detection of exon 19 deletions or exon 21 (L858R) substitution mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene to identify patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) eligible for treatment with Tarceva (erlotinib). The test is already approved for using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue specimens, and this new use is for detection of these specific mutations in circulating-free tumor DNA (cfDNA) isolated from plasma specimens (liquid biopsy specimens). cobas® EGFR Mutation test v2 is marketed by Roche Molecular Systems, Inc. in Pleasanton, California.19
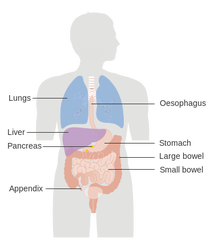 Figure 10. Neuroendocrine tumor regions21
Figure 10. Neuroendocrine tumor regions21
- Netspot, June 1, 2016: A new diagnostic imaging agent, Netspot was approved by the FDA to detect tumors in adult and pediatric patients with the rare condition, somatostatin receptor positive neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) (Fig. 10). Netspot is the first kit for the preparation of a radioactive diagnostic agent gallium Ga 68 dotatate. NETs are rare non-cancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant) tumors that develop in the hormone cells of neuroendocrine system found in organs such as stomach, intestines, pancreas, lungs and others. Somatostatin is a hormone that regulates the endocrine system, and NETs have receptors for somatostatin. Ga 68 dotatate binds to these receptors as a positron emitting anologue of somatostatin. Netspot is marketed by Advanced Accelerator Applications USA, Inc.20
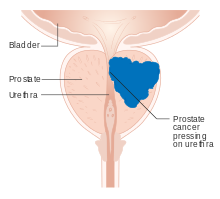 Figure 11. Prostate cancer23
Figure 11. Prostate cancer23
- Axumin, May 27, 2016: Axumin, a new radioactive diagnostic imaging agent, was approved to detect recurrent prostate cancer (Fig. 11) in patients who have been treated for prostate cancer but have persistently high prostate specific antigen (PSA) 22. High PSA blood levels of these patients are a suspicious sign that cancer is coming back or spreading. Axumin is marketed by Blue Earth Diagnostics, Ltd., Oxford, United Kingdom.
Prostate cancer
Early diagnosis procedures: Prostate cancer
- Tecentriq (atezolizumab), May 18, 2016: Tecentriq (atezolizumab) (see above) was approved to treat urothelial carcinoma. Urethelial carcinoma is the most common type of bladder cancer and occurs in the urinary tract system, including the bladder and related organs24. Tecentriq is approved for treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma whose disease has worsened during or following platinium-containing chemotherapy, or within 12 months of receiving platinium containing chemotherapy, either before (nonadjuvant) or after (adjuvant) surgical treatment. The FDA also approved the Ventana PD-L1 (SP142) assay to detect PD-L1 protein expression levels on patients’ tumor-infiltrating immune cells to determine the patients who are more likely to respond to treatment with Tecentriq. Tecentriq is marketed by Genentech based in San Francisco, California. The Ventana PD-L1 (SP142) assay complementary diagnostic test for Tecentriq is marketed by Ventana Medical Systems, based in Tuscon, Arizona.24
- Opdivo (nivolumab), May 17, 2016: The FDA granted an accelerated approval for Opdivo (nivolumab) (see above) for the treatment of patients with classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma (cHL) that has relapsed or progressed after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) and post-transplantation brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris).25
What is HODGKIN'S LYMPHOMA?
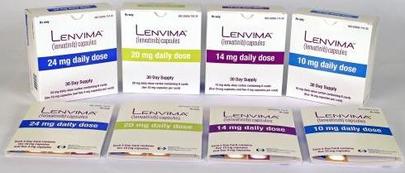 Figure 12. Lenvima (lenvatinib)
Figure 12. Lenvima (lenvatinib)
- Lenvima (lenvatinib), May 13, 2016: The FDA approved Lenvima (lenvatinib) in combination with everolimus, for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (Fig. 6) following one prior anti-angiogenic therapy26. Renal cell carcinoma is the most common form of kidney cancer that forms in the tissues of the kidney that make urine. Lenvatinib is a multityrosine kinase inhibitor, which inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors.27 VEGF has a role in angiogenesis, a system that provides nutrition and oxygen to tumor cells through blood vessels. Lenvima is a kinase inhibitor, which inhibits certain proteins from helping cancer cells to grow and divide.30 Lenvima is marketed by Eisai, Inc. in Woodcliff Lake, New Jersey.26
 Figure 13. Cabometyx (cabozantinib)
Figure 13. Cabometyx (cabozantinib)
- Cabometyx (cabozantinib), April 11, 2016: Cabometyx (cabozantinib) was approved for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (Fig. 6) in patients who have received prior anti-angiogenic therapy29. Cabozantinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets VEGF receptor and inhibits tumor development. VEGF is found increased in renal cell carcinoma.30 Cabometyx is marketed by Exelixis, Inc. South San Francisco, California.
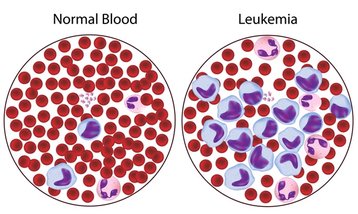 Figure 14. Leukemia
Figure 14. Leukemia
- Venclexta (venetoclax), April 11, 2016: Venclexta (venetoclax) was approved to treat patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) (Fig. 14) who have a chromosomal abnormality called 17p deletion and who have been treated with at least one prior CLL therapy31. The chrosomal part of 17p includes B-cell lymphoma 2 (BLC-2) protein region. BCL2 is an anti-apoptotic (anti-cell death) protein that provides resistance to CLL cells for apoptosis (programmed cell death) and found increased in CLL. Venetoclax targets the B-cell lymphoma 2 (BLC-2) protein.32 CLL is characterized by the progressive accumulation is abnormal lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). CLL patients with 17p deletion lack a portion of the chromosome that acts to suppress cancer growth. 17p deletion is confirmed by a companion diagnostic Vysis CLL FISH probe kit. Venclexta is manufactured by AbbVie Inc. of South San Francisco, California. The Vysis CLL FISH probe kit is manufactured by Abbott Molecular of Des Plaines, Illinois.31
CANCER TYPES
 Figure 15. Xalkori (crizotinib)
Figure 15. Xalkori (crizotinib)
- Xalkori (crizotinib), March 11, 2016: Xalkori (crizotinib) was approved for the treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (Fig. 4) whose tumors are ROS1-positive.33 Xalkori was first approved in 2011 for the treatment of patients whose tumors are anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive.34 Crizotinib is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor. RTKs are involved in cell proliferation, migration, metabolism, differentiation, and survival, thus their activity is strictly controlled in normal cells. Xalkori inhibits RTKs including the protein produced by abnormal ALK and ROS1 genes.35 Xalkori is marketed by Pfizer, Inc. New York City, New York.
 Figure 16. Afinitor (everolimus)
Figure 16. Afinitor (everolimus)
- Afinitor (everolimus), February 26, 2016: Afinitor (everolimus) was approved for the treatment of adult patients with progressive, well-differentiated non-functional, neuroendocrine tumors (NET) (Fig. 8) of gastrointestinal (GI) or lung origin with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic disease.36 Everolimus is a kinase inhibitor of mammalian rapamycin (mTOR) and inhibits the growth of tumor cells. The mTOR pathway regulates cell cycle and is dysregulated in several human cancers.37 Afilitor is marketed by Novartis based in Basel, Switzerland.
 Figure 17. Gazyva (obinutuzumab)
Figure 17. Gazyva (obinutuzumab)
- Gazyva (obinutuzumab), February 26, 2016: Gazyva (obinutuzumab), a cancer immunotherapy drug, was approved for the use in combination with bendamustine followed by obinutuzumab monotherapy for the treatment of patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) who relapsed after, or are refractory to, a rituximab-containing regimen.38 Obinutuzumab is a monoclonal antibody against CD20, helping cells of the immune system to attack cancer cells.39 Gazyva is marketed by Genentech, Inc. South San Francisco, California.
 Figure 18. Ibrance (palbociclib)
Figure 18. Ibrance (palbociclib)
- Ibrance (palbociclib), February 19, 2016: Ibrance (palbociclib) was approved in combination with fulvestrant for the treatment with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer with disease progression following endocrine therapy.40,41 Palbociclib is a selective kinase inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) 4 and 6, which are involved in promoting the growth of cancer cells.42 Ibrance is marketed by Pfizer, Inc. New York City, New York.
BREAST CANCER SYMPOSIUM TAKEAWAYS & NUTRITION GUIDANCE
Dr. Chen's Talk on Breast Cancer Early Detection & Prevention
Early diagnosis procedures: Breast cancer
 Figure 19. Halaven (eribulin)
Figure 19. Halaven (eribulin)
- Halaven (eribulin), January 28, 2016: Halaven (eribulin) was approved for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic liposarcoma who have received a prior anthracycline-containing regimen.43 Soft tissue sarcoma (STS) is a disease in which cancer cells form in the soft tissues of the body, including the muscles, tendons, fat, blood vessels, nerves and tissues around joints. Liposarcoma is a specific type of STS that occurs in fat cells. Eribulin is a tubulin (a component of cell skeleton) polymerization inhibitor leading to apoptosis (programmed cell death) of cancer cells.44 Halaven is marketed by Eisai based in Woodcliff Lake, New Jersey.
 Figure 20. Arzerra (oftatumumab)
Figure 20. Arzerra (oftatumumab)
- Arzerra (oftatumumab), January 19, 2016: Arzerra (oftatumumab), a cancer immunotherapy drug, was approved for extended treatment of patients who are in complete or partial response after at least two lines of therapy for recurrent or progressive chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) (Fig. 12).45 CLL arises from a group of white blood cells known as B-cells that are part of the body’s immune system. Arzerra is a novel monoclinal antibody against CD20 (a protein found on the surface of both normal and malignant B cells), and induces immune system cells to kill tumor cells.46 Arzerra is marketed by Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation in Basel, Switzerland.
References:
1. FDA grants accelerated approval to new treatment for advanced ovarian cancer. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm533873.htm. Accessed January 11, 2017.
2. BRCA 1 gene. https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/gene/BRCA1
3. Daratumumab (DARZALEX). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm530249.htm. Accessed January 11, 2017.
4. Lokhorst HM, Plesner T, Laubach JP, et al. Targeting CD38 with Daratumumab Monotherapy in Multiple Myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(13):1207-1219.
5. FDA approves Darzalex for patients with previously treated multiple myeloma. 2015. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm472875.htm. Accessed January 11, 2017.
6. Nivolumab for SCCHN. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm528920.htm. Accessed January 11, 2017.
7. Johnson DB, Peng C, Sosman JA. Nivolumab in melanoma: latest evidence and clinical potential. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2015;7(2):97-106.
8. FDA approves Keytruda for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. http://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm465444.htm. Accessed January 11, 2017.
9. Pembrolizumab (KEYTRUDA) Checkpoint Inhibitor. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm526430.htm. Accessed January 11, 2017.
10. Vachhani P, Chen H. Spotlight on pembrolizumab in non-small cell lung cancer: the evidence to date. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:5855-5866. doi:10.2147/OTT.S97746.
11. Non Small Cell Lung Cancer - Health, Medicine and Anatomy Reference Pictures. http://healthfavo.com/non-small-cell-lung-cancer.html. Accessed January 13, 2017.
12. FDA grants accelerated approval to new treatment for advanced soft tissue sarcoma. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm525878.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
13. Tap WD, Jones RL, Van Tine BA, et al. Olaratumab and doxorubicin versus doxorubicin alone for treatment of soft-tissue sarcoma: an open-label phase 1b and randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2016;388(10043):488-497. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30587-6.
14. Erlotinib (Tarceva). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm525739.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
15. Kobayashi K, Hagiwara K. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation and personalized therapy in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Target Oncol. 2013;8(1):27-33. doi:10.1007/s11523-013-0258-9.
16. Atezolizumab (TECENTRIQ). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm525780.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
17. Modification of the Dosage Regimen for Nivolumab. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm520871.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
18. Pembrolizumab (KEYTRUDA). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm515627.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
19. cobas®EGFR Mutation Test v2. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm504540.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
20. FDA approves new diagnostic imaging agent to detect rare neuroendocrine tumors. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm504524.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
21. Wikimedia.org
22. FDA approves new diagnostic imaging agent to detect recurrent prostate cancer. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm503920.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
23. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prostate_cancer
24. FDA approves new, targeted treatment for bladder cancer. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm501762.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
25. Nivolumab (Opdivo) for Hodgkin Lymphoma. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm501412.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
26. Lenvatinib in combination with Everolimus. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm501070.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
27. Inoue K, Mizuo H, Kawaguchi S, Fukuda K, Kusano K, Yoshimura T. Oxidative Metabolic Pathway of Lenvatinib Mediated by Aldehyde Oxidase. Drug Metab Dispos. 2014;42(8).
28. FDA approves Lenvima for a type of thyroid cancer. http://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm434288.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
29. Cabozantinib (CABOMETYX). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm497483.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
30. Choueiri TK, Escudier B, Powles T, et al. Cabozantinib versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(19):1814-1823.
31. FDA approves new drug for chronic lymphocytic leukemia in patients with a specific chromosomal abnormality. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm495253.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
32. Roberts AW, Davids MS, Pagel JM, et al. Targeting BCL2 with Venetoclax in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(4):311-322. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1513257.
33. FDA expands use of Xalkori to treat rare form of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm490329.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
34. FDA approves Xalkori with companion diagnostic for a type of late-stage lung cancer. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm269856.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
35. Cui JJ, Tran-Dubé M, Shen H, et al. Structure Based Drug Design of Crizotinib (PF-02341066), a Potent and Selective Dual Inhibitor of Mesenchymal–Epithelial Transition Factor (c-MET) Kinase and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK). J Med Chem. 2011;54(18):6342-6363. doi:10.1021/jm2007613.
36. Everolimus (Afinitor). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm488028.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
37. Formica RN, Lorber KM, Friedman AL, et al. The evolving experience using everolimus in clinical transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2004;36(2 Suppl):495S-499S. doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2004.01.015.
38. Obinutuzumab. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm488013.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
39. Evans SS, Clemmons AB. Obinutuzumab: A Novel Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2015;6(4):370-374. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26705497.
40. Palbociclib (IBRANCE Capsules). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm487080.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
41. FDA approves Ibrance for postmenopausal women with advanced breast cancer. http://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm432871.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
42. Finn RS, Dering J, Conklin D, et al. PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, preferentially inhibits proliferation of luminal estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(5):R77. doi:10.1186/bcr2419.
43. Eribulin. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm483795.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
44. Towle MJ, Salvato KA, Budrow J, et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Anticancer Activities of Synthetic Macrocyclic Ketone Analogues of Halichondrin B. Cancer Res. 2001;61(3).
45. Ofatumumab (Arzerra Injection). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm482308.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
46. Lin TS. Ofatumumab: a novel monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2010;3:51-59. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23226042.
1. FDA grants accelerated approval to new treatment for advanced ovarian cancer. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm533873.htm. Accessed January 11, 2017.
2. BRCA 1 gene. https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/gene/BRCA1
3. Daratumumab (DARZALEX). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm530249.htm. Accessed January 11, 2017.
4. Lokhorst HM, Plesner T, Laubach JP, et al. Targeting CD38 with Daratumumab Monotherapy in Multiple Myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(13):1207-1219.
5. FDA approves Darzalex for patients with previously treated multiple myeloma. 2015. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm472875.htm. Accessed January 11, 2017.
6. Nivolumab for SCCHN. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm528920.htm. Accessed January 11, 2017.
7. Johnson DB, Peng C, Sosman JA. Nivolumab in melanoma: latest evidence and clinical potential. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2015;7(2):97-106.
8. FDA approves Keytruda for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. http://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm465444.htm. Accessed January 11, 2017.
9. Pembrolizumab (KEYTRUDA) Checkpoint Inhibitor. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm526430.htm. Accessed January 11, 2017.
10. Vachhani P, Chen H. Spotlight on pembrolizumab in non-small cell lung cancer: the evidence to date. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:5855-5866. doi:10.2147/OTT.S97746.
11. Non Small Cell Lung Cancer - Health, Medicine and Anatomy Reference Pictures. http://healthfavo.com/non-small-cell-lung-cancer.html. Accessed January 13, 2017.
12. FDA grants accelerated approval to new treatment for advanced soft tissue sarcoma. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm525878.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
13. Tap WD, Jones RL, Van Tine BA, et al. Olaratumab and doxorubicin versus doxorubicin alone for treatment of soft-tissue sarcoma: an open-label phase 1b and randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2016;388(10043):488-497. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30587-6.
14. Erlotinib (Tarceva). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm525739.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
15. Kobayashi K, Hagiwara K. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation and personalized therapy in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Target Oncol. 2013;8(1):27-33. doi:10.1007/s11523-013-0258-9.
16. Atezolizumab (TECENTRIQ). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm525780.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
17. Modification of the Dosage Regimen for Nivolumab. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm520871.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
18. Pembrolizumab (KEYTRUDA). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm515627.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
19. cobas®EGFR Mutation Test v2. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm504540.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
20. FDA approves new diagnostic imaging agent to detect rare neuroendocrine tumors. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm504524.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
21. Wikimedia.org
22. FDA approves new diagnostic imaging agent to detect recurrent prostate cancer. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm503920.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
23. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prostate_cancer
24. FDA approves new, targeted treatment for bladder cancer. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm501762.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
25. Nivolumab (Opdivo) for Hodgkin Lymphoma. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm501412.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
26. Lenvatinib in combination with Everolimus. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm501070.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
27. Inoue K, Mizuo H, Kawaguchi S, Fukuda K, Kusano K, Yoshimura T. Oxidative Metabolic Pathway of Lenvatinib Mediated by Aldehyde Oxidase. Drug Metab Dispos. 2014;42(8).
28. FDA approves Lenvima for a type of thyroid cancer. http://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm434288.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
29. Cabozantinib (CABOMETYX). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm497483.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
30. Choueiri TK, Escudier B, Powles T, et al. Cabozantinib versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(19):1814-1823.
31. FDA approves new drug for chronic lymphocytic leukemia in patients with a specific chromosomal abnormality. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm495253.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
32. Roberts AW, Davids MS, Pagel JM, et al. Targeting BCL2 with Venetoclax in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(4):311-322. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1513257.
33. FDA expands use of Xalkori to treat rare form of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm490329.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
34. FDA approves Xalkori with companion diagnostic for a type of late-stage lung cancer. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm269856.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
35. Cui JJ, Tran-Dubé M, Shen H, et al. Structure Based Drug Design of Crizotinib (PF-02341066), a Potent and Selective Dual Inhibitor of Mesenchymal–Epithelial Transition Factor (c-MET) Kinase and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK). J Med Chem. 2011;54(18):6342-6363. doi:10.1021/jm2007613.
36. Everolimus (Afinitor). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm488028.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
37. Formica RN, Lorber KM, Friedman AL, et al. The evolving experience using everolimus in clinical transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2004;36(2 Suppl):495S-499S. doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2004.01.015.
38. Obinutuzumab. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm488013.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
39. Evans SS, Clemmons AB. Obinutuzumab: A Novel Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2015;6(4):370-374. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26705497.
40. Palbociclib (IBRANCE Capsules). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm487080.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
41. FDA approves Ibrance for postmenopausal women with advanced breast cancer. http://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm432871.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
42. Finn RS, Dering J, Conklin D, et al. PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, preferentially inhibits proliferation of luminal estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(5):R77. doi:10.1186/bcr2419.
43. Eribulin. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm483795.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
44. Towle MJ, Salvato KA, Budrow J, et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Anticancer Activities of Synthetic Macrocyclic Ketone Analogues of Halichondrin B. Cancer Res. 2001;61(3).
45. Ofatumumab (Arzerra Injection). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm482308.htm. Accessed January 12, 2017.
46. Lin TS. Ofatumumab: a novel monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2010;3:51-59. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23226042.
The Journal of Simplified Cancer Research (JSCR) is the official journal of Cancer Research Simplified. For only $4.99 per monthly issue, [or a discounted $49.99 per year], you can gain digital access to straightforward information and articles on cancer news, diagnosis, prevention, treatment, and clinical trials. Fill out the form, make your payment, and you'll receive your copy right in your inbox! To get your copy now on The Journal of Simplified Cancer Research (JSCR) page.
Please donate to support our cause - help us continue with our trusted educational programs:
Cancer Education and Research Institute, fka Cancer Research Simplified, is a registered 501(c)(3) non-profit organization.
Your donations are tax deductible to the extent permitted by law.
Your donations are tax deductible to the extent permitted by law.











