CERI Cancer Education Programs
All you need to know about cancer
Cancer detection methods:
- Biopsy
- Blood test
- Computer tomography (CT)
- Magnetic resonance tomography (MRI)
- Positron electron topography (PET, or PET Scan)
- Ultrasound
- X-ray
- Thermography
- Surgery
Biopsy
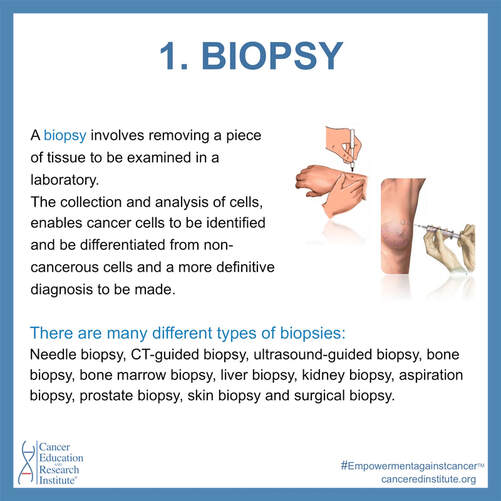
A Biopsy involves removing a piece of tissue to be examined in a laboratory. The collection and analysis of cells, enables cancer cells to be identified and be differentiated from non-cancerous cells and a more definitive diagnosis to be made.
There are many different types of biopsies:
Needle biopsy, CT-guided biopsy, ultrasound-guided biopsy, bone biopsy, bone marrow biopsy, liver biopsy, kidney biopsy, aspiration biopsy, prostate biopsy,
skin biopsy and surgical biopsy.
There are many different types of biopsies:
Needle biopsy, CT-guided biopsy, ultrasound-guided biopsy, bone biopsy, bone marrow biopsy, liver biopsy, kidney biopsy, aspiration biopsy, prostate biopsy,
skin biopsy and surgical biopsy.
Blood test
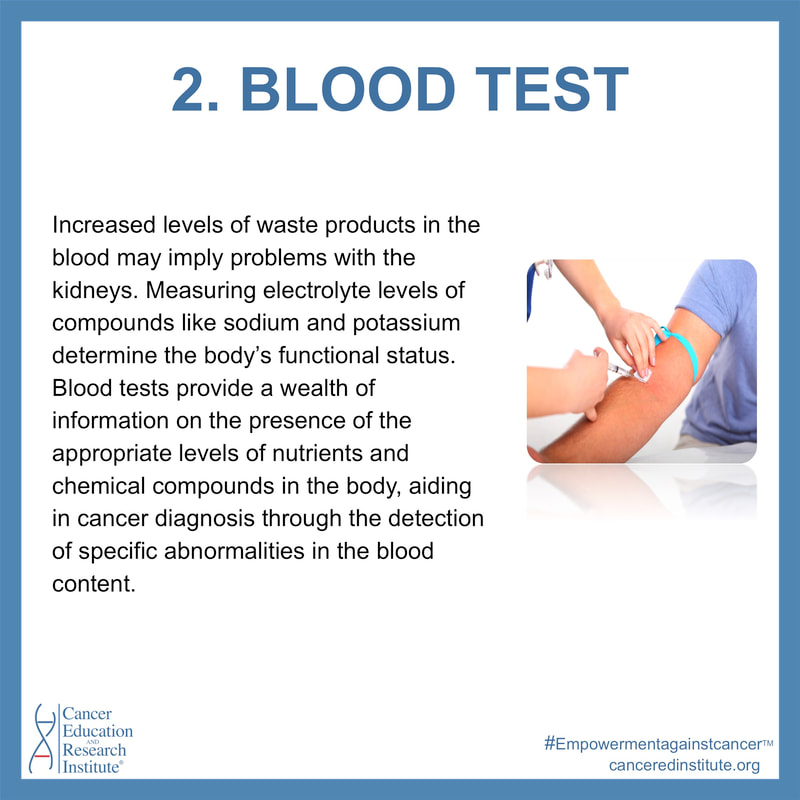
Blood tests can be extremely useful as they evaluate levels of essential molecules such as sugars, fats, proteins and DNA and enable doctors to associate
abnormal levels with specific cancers. Complete Blood Counts (CBC) are commonly used as all-encompassing measurements of the body’s health; they measures size, number, and maturity of blood cells in a specific volume of blood.
Increased levels of waste products in the blood may imply problems with the kidneys. Measuring electrolyte levels of compounds like sodium and potassium determine the body’s functional status. Blood tests provide a wealth of information on the presence of the appropriate levels of nutrients and chemical compounds in the body, aiding in cancer diagnosis through the detection of specific abnormalities in the blood content.
abnormal levels with specific cancers. Complete Blood Counts (CBC) are commonly used as all-encompassing measurements of the body’s health; they measures size, number, and maturity of blood cells in a specific volume of blood.
Increased levels of waste products in the blood may imply problems with the kidneys. Measuring electrolyte levels of compounds like sodium and potassium determine the body’s functional status. Blood tests provide a wealth of information on the presence of the appropriate levels of nutrients and chemical compounds in the body, aiding in cancer diagnosis through the detection of specific abnormalities in the blood content.
Computer tomography (CT)
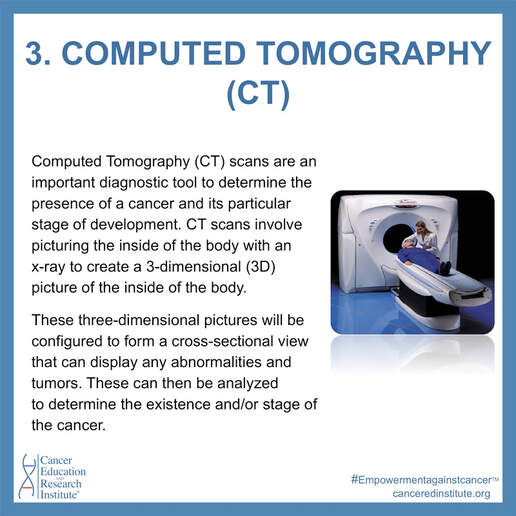
Computed Tomography (CT) scans are an important diagnostic tool to determine the presence of a cancer and its particular stage of development. CT scans involve picturing the inside of the body with an x-ray to create a 3-dimensional (3D) picture of the inside of the body. These three-dimensional pictures will be configured to form a cross-sectional view that can display any abnormalities and tumors. These can then be analyzed to determine the existence and/or stage of the cancer. This test is not physically demanding, lasting for no longer than an hour, and allows patients to return to their daily activities immediately after.
Magnetic resonance tomography (MRI)
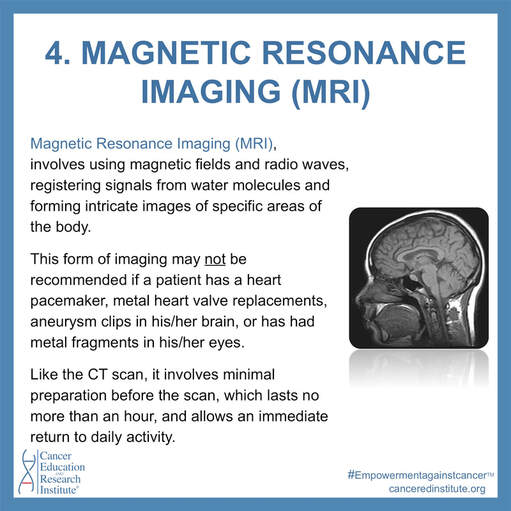
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), involves using magnetic fields and radio waves, registering signals from water molecules and forming intricate images of specific areas of the body. This form of imaging may not be recommended if a patient has a heart pacemaker, metal heart valve replacements, aneurysm clips in his/her brain, or has had metal fragments in his/her eyes. Like the CT scan, it involves minimal preparation before the scan, which lasts no more than an hour, and allows an immediate return to daily activity.
Positron electron topography (PET, or PET Scan)
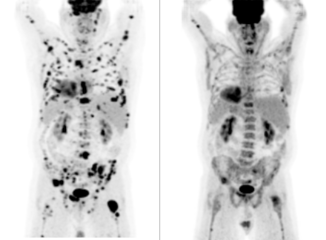
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) involves injecting radioactive tracer into the vein of a patient. The tracer commonly used is a radioactive form of glucose. This is effective since cancer, maintaining the continuous division of cells, increases the metabolism of glucose.
PET imaging allows physicians to examine the way glucose is being metabolized in the body, and thus may be an indicator of cancer.
PET imaging allows physicians to examine the way glucose is being metabolized in the body, and thus may be an indicator of cancer.
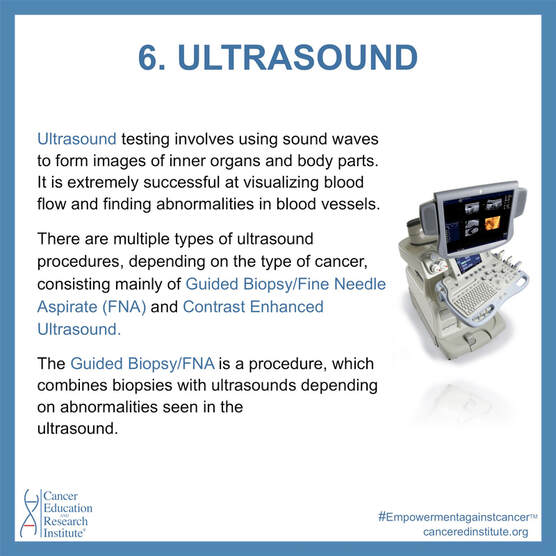
Ultrasound
Ultrasound Testing involves using sound waves to form images of inner organs and body parts. It is extremely successful at visualizing blood flow and finding abnormalities in blood vessels. There are multiple types of ultrasound procedures, depending on the type of cancer, consisting mainly of Guided Biopsy/fine needle aspirate (FNA) and Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound.
The Guided Biopsy/FNA is a procedure, which combines biopsies with ultrasounds depending on abnormalities seen in the ultrasound.
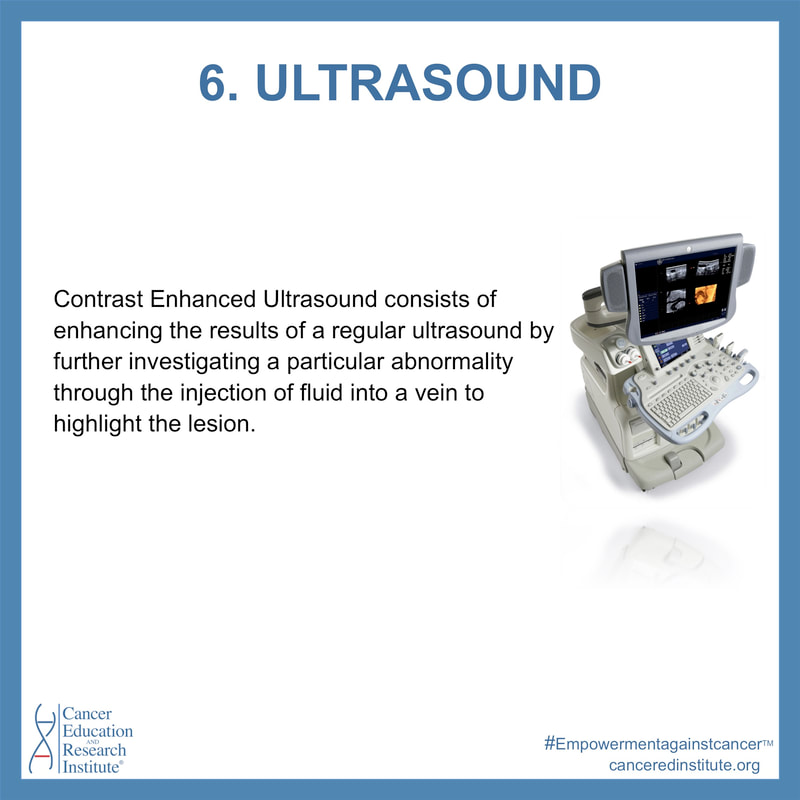
Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound consists of enhancing the results of a regular ultrasound by further investigating a particular abnormality through the injection of fluid into a vein to highlight the lesion.
The Guided Biopsy/FNA is a procedure, which combines biopsies with ultrasounds depending on abnormalities seen in the ultrasound.
Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound consists of enhancing the results of a regular ultrasound by further investigating a particular abnormality through the injection of fluid into a vein to highlight the lesion.
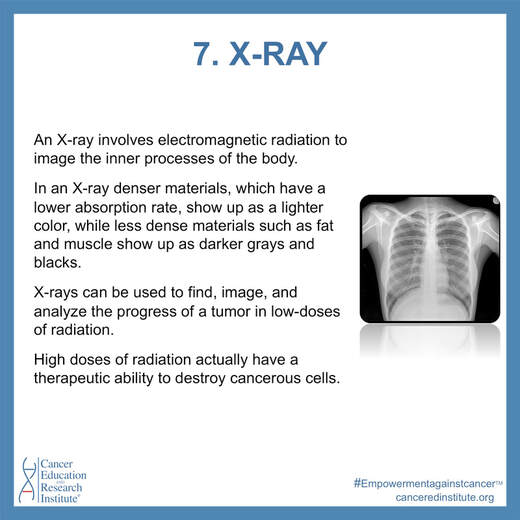
X-ray
An X-ray involves electromagnetic radiation to image the inner processes of the body.
In an X-ray denser materials, which have a lower absorption rate, show up as a lighter color, while less dense materials such as fat and muscle show up as
darker grays and blacks.
X-rays can be used to find, image, and analyze the progress of a tumor in low-doses of radiation. High doses of radiation actually have a therapeutic ability to destroy cancerous cells.
In an X-ray denser materials, which have a lower absorption rate, show up as a lighter color, while less dense materials such as fat and muscle show up as
darker grays and blacks.
X-rays can be used to find, image, and analyze the progress of a tumor in low-doses of radiation. High doses of radiation actually have a therapeutic ability to destroy cancerous cells.
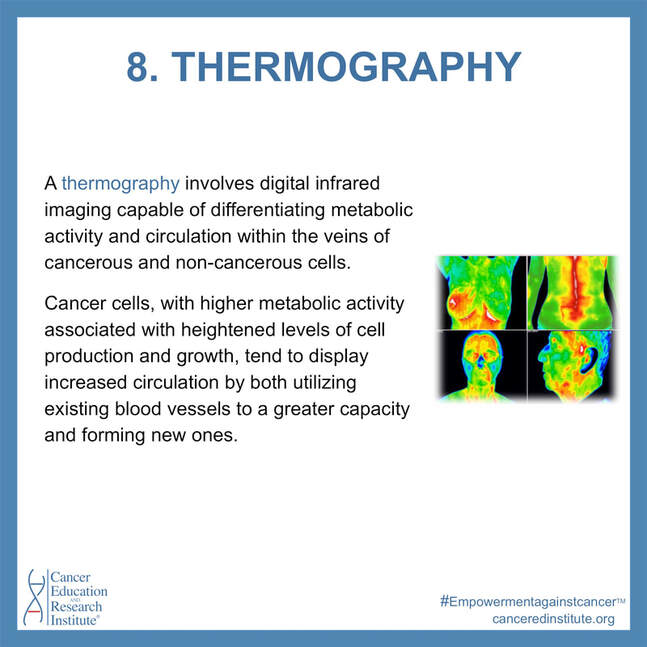
Thermography
A thermography involves digital infrared imaging capable of differentiating metabolic activity and circulation within the veins of cancerous and non-cancerous cells. Cancer cells, with higher metabolic activity associated with heightened levels of cell production and growth, tend to display increased circulation by both utilizing existing blood vessels to a greater capacity and forming new ones. These differing circulations create different surface temperatures in diverse areas of the body, which can be detected and analyzed using infrared cameras.
Thermographies are extremely useful not only in detecting already existing cancer, but also in showing pre-cancerous states, a unique and vital ability.
BONUS: Learn about Thermography in all detail from our partner, Boston Thermography Center - click here.
Thermographies are extremely useful not only in detecting already existing cancer, but also in showing pre-cancerous states, a unique and vital ability.
BONUS: Learn about Thermography in all detail from our partner, Boston Thermography Center - click here.
Surgery
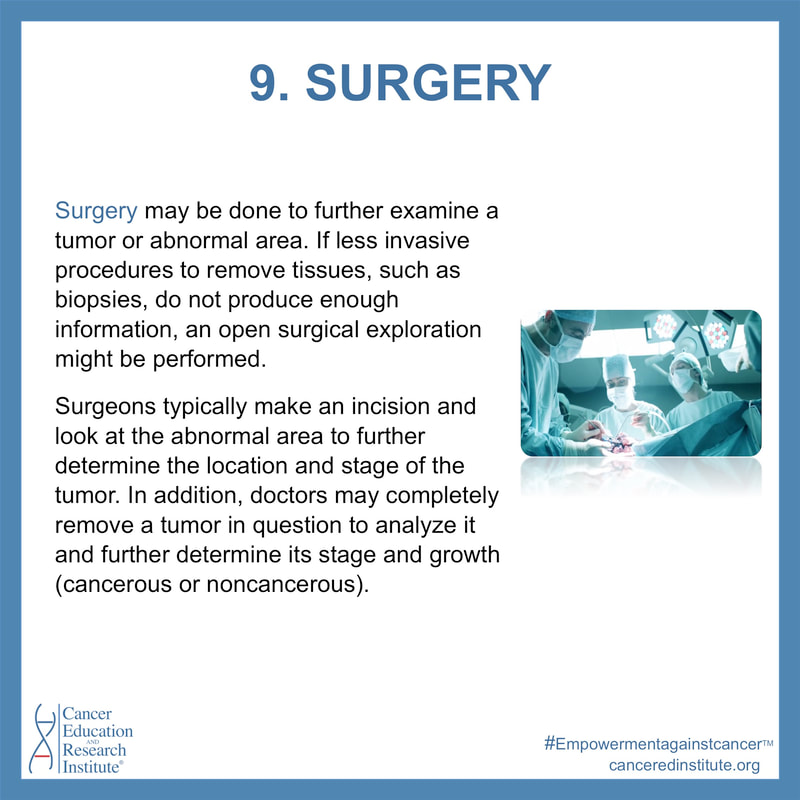
Surgery may be done to further examine a tumor or abnormal area. If less invasive procedures to remove tissues, such as biopsies, do not produce enough information, an open surgical exploration might be performed.
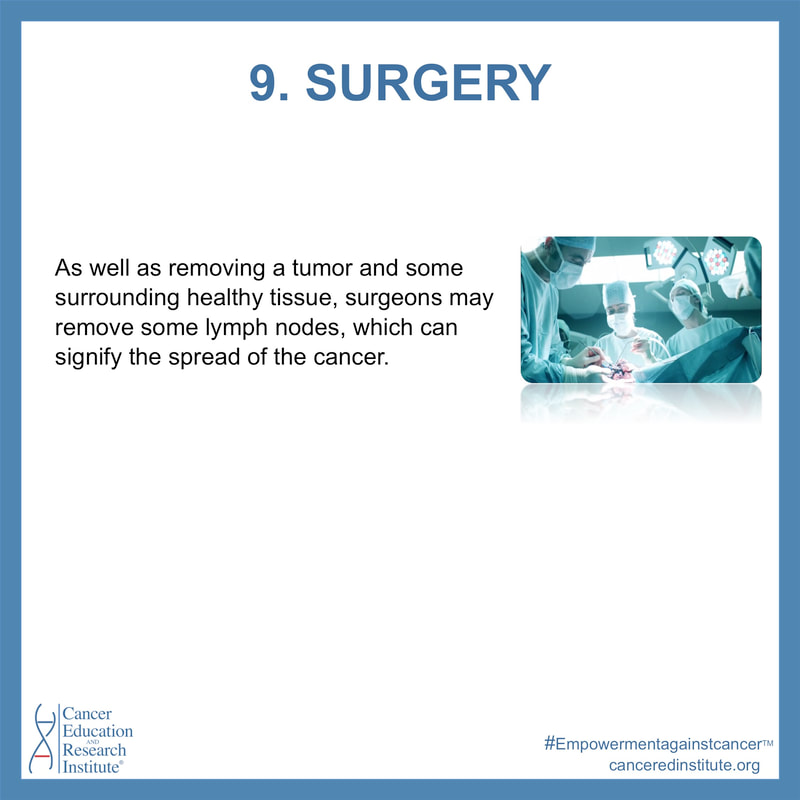
Surgeons typically make an incision and look at the abnormal area to further determine the location and stage of the tumor. In addition, doctors may completely remove a tumor in question to analyze it and further determine its stage and growth (cancerous or noncancerous). As well as removing a tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue, surgeons may remove some lymph nodes, which can signify the spread of the cancer.
Surgeons typically make an incision and look at the abnormal area to further determine the location and stage of the tumor. In addition, doctors may completely remove a tumor in question to analyze it and further determine its stage and growth (cancerous or noncancerous). As well as removing a tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue, surgeons may remove some lymph nodes, which can signify the spread of the cancer.
You might also like to:
Watch our cancer videos |
Read our cancer articles |
All about cancer types |
Thank you for your support to help us continue with our educational programs,
highly sought after worldwide.
highly sought after worldwide.